Public Health Corner: The Difficulty of Treating Foodborne Enterohemorrhagic E. coli Infections

Image credit: Selvanegra/iStock/Getty Images Plus via Getty Images
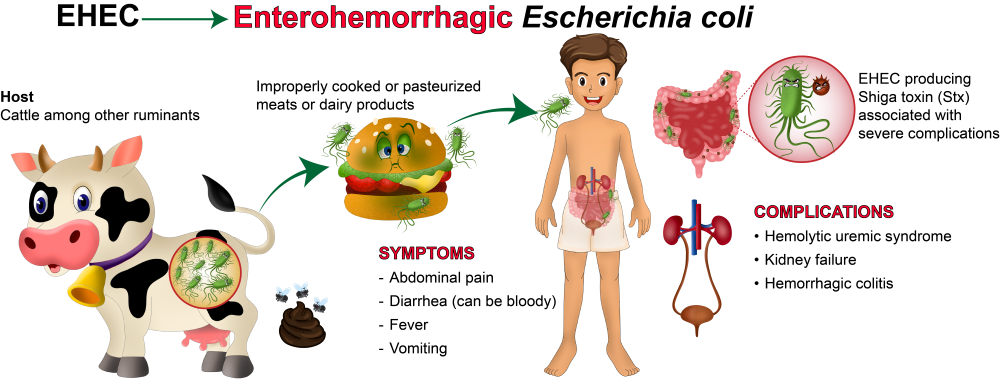
Ingestion of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 (EHEC) bacteria can occur after eating contaminated food, such as hamburger meat that has not been properly cooked. EHEC has also been responsible for outbreaks associated with contaminated food or vegetables. Consumption of contaminated food can cause infected people to have different symptoms. EHEC-associated infections often begin with bloody diarrhea, but can lead to much more dangerous outcomes like kidney failure and death via hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS).

EHEC Infection Symptoms
EHEC bacteria is commonly found in the gut of cows, although it does not sicken cattle (Figure 1). However, the bacteria can end up in the environment when it is excreted in fecal matter. One of the main sources of EHEC that can lead to disease is the consumption of contaminated meat that is not properly cooked. EHEC can also be acquired from vegetables contaminated with cow fecal matter. Once ingested, the bacteria can survive in the human gut and "colonize" the large intestine, leading to diarrhea. The illness can become more complicated and dangerous when the bacteria produce Shiga toxin, which leads to kidney cell death and damage of the kidneys.
Shiga Toxin Production
When EHEC colonizes the human intestine, the bacteria protect themselves by creating a small, cup-shaped houses or "pedestals" constructed from the human intestinal cells (Figure 2).

Once the EHEC colonizes and resides in the human intestine, it leads to diarrhea in infected people. When a person infected with EHEC is treated with antibiotics, which would normally kill the bacteria, it can lead to an alarm response in the bacteria (also known as an "SOS response") and cause them to produce more Shiga toxin. For this reason, EHEC bacterial infections should not be treated with antibiotic therapy. EHEC outbreaks throughout the world are often fatal, and there is a need for more therapeutic options to treat EHEC infections.

E. coli Habitat and Relatives
EHEC is a relative of other E. coli bacteria, which are found in many different types of environments. Normally, E. coli species are not pathogenic or dangerous to humans, and often live in the gut and help digest food. However, some E. coli species have gained virulence factors that allow them to produce illness in humans. E. coli bacteria are classified based on their virulence factors and the type of illness they cause. For example, enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC), enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), and adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) are different subtypes of E. coli associated with human disease. A unique characteristic of EHEC—and something that makes it particularly dangerous—is its ability to produce Shiga toxin in the human host, which can lead to death.
EHEC is a Dangerous Microbe
EHEC bacteria can sicken adults, as well as children. In the U.S., there have been outbreaks of infections in people who have consumed contaminated food products; however, many people have not heard of EHEC because it is a relatively rare form of E. coli to cause illness in the U.S. Worldwide, however, children—particularly those in low-income countries with limited access to therapies—are especially vulnerable to EHEC infections and can develop severe illness.

Scientists and public health personnel are investigating new ways to combat EHEC-associated infections, including the potential development of efficient vaccines and alternative therapies that do not involve common antibiotics.
Looking for quick answers on food safety topics?
Try Ask FSM, our new smart AI search tool.
Ask FSM →
Authors
Javier Sanchez-Villamil works with the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas and the Research Center for Applied Science and Advance Technology (CICATA) at the National Polytechnic Institute in Querétaro, Mexico.
Daniel Tapia works with the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas.
Alfredo G. Torres is the Herman Barnett Distinguished Professor in Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas.








