Applying Industry 4.0 to Food Safety
The opportunities for strengthening food safety through the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies across the food supply chain are vast

After mechanization (steam engine), industrialization (introduction of electricity and production lines), and automation (electronics and robotics), the World Economic Forum defined the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Figure 1) as being "characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres."1
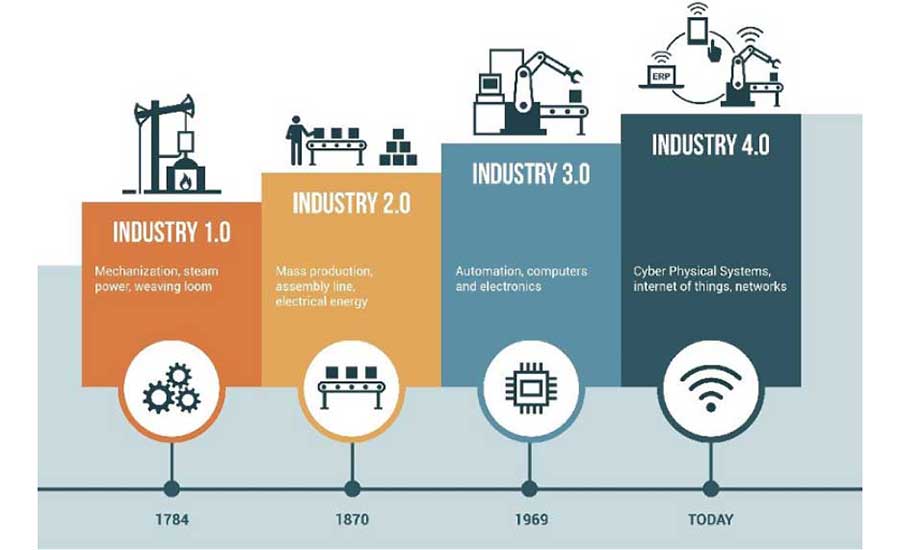
Industry 4.0 relies on a wide group of disruptive technologies such as:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Blockchain
- Advanced analytics
- Machine learning
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Simulation.
However, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is about more than just technology-driven change. It is an opportunity to help everyone, including industry leaders, policymakers, as well as the public at large to harness converging technologies to create an inclusive, human-centered future.
Particularly in the case of the food sector, these new technologies can be used to make food safer. This article aims to provide:
- A brief description about how this is being (and can be) done
- How Industry 4.0 technologies are currently being applied across different links of the food supply chain
- A methodology for implementing a strong and effective Industry 4.0 strategy within a food business
- An outline of the potential benefits of Industry 4.0 to help drive food safety forward.
Industry 4.0 Maturity Levels
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies across the food industry is still in its infancy. Based on industry-wide studies, adoption across the food sector ranges from 20–40 percent, while the oil and gas sector has seen an uptake of over 80 percent, and the automotive industry has witnessed uptake of 45–60 percent.
When speaking about technology adoption, we mean general adoption in food, not specifically related to food safety. There is still a long way to go, and as a sector, we have a great opportunity to accelerate the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. Furthermore, we have an opportunity to learn from other sectors' experience, such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and IT to transition more quickly toward Industry 4.0 technologies.
There are four maturity levels in the implementation of Industry 4.0 to achieve better food safety, as illustrated in Figure 2. These maturity levels encompass digitization (automating data), digitalization (integrating systems and data flows), automation (reducing human error through automated tasks), and culture (change in business mindset from reactive to preventive, proactive, and ultimately predictive).
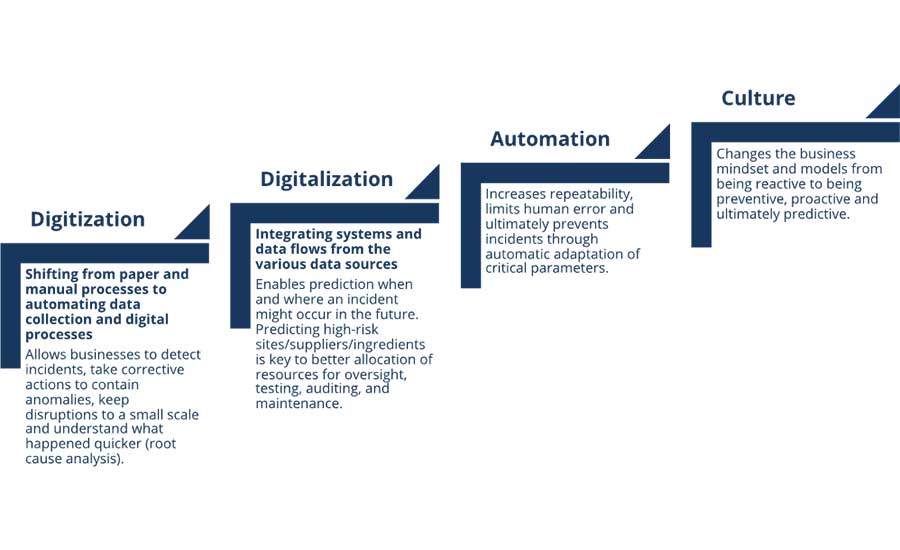
At present, the food industry is embracing digitization. Predictive analytics is still in its infancy and is struggling with data integration, limiting the ability for food businesses to truly leverage its full potential. Automation to prevent incidents is applied only in a very localized way, and is rarely deployed to leverage data as an additional source of revenue.
Industry 4.0 Across the Food Supply Chain
The opportunities for strengthening food safety through the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies across the food supply chain are vast. Nonetheless, the applicability varies greatly depending on which part of the food supply chain you operate in, as do the potential benefits.
Looking for quick answers on food safety topics?
Try Ask FSM, our new smart AI search tool.
Ask FSM →
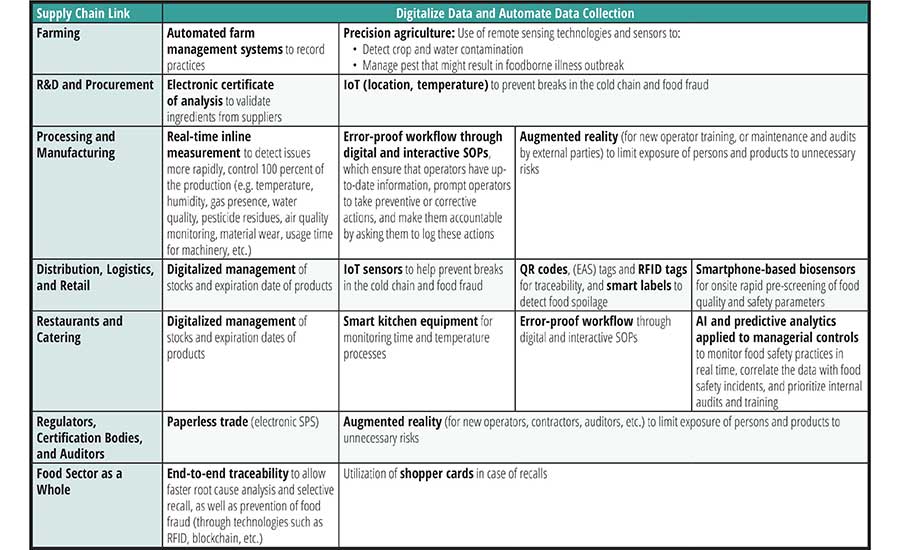
Table 1 illustrates some of the adoptions of Industry 4.0 technologies for food safety, particularly related to data, that we are starting to see emerging across different parts of the food supply chain.
How to Implement Industry 4.0 Technologies for Food Safety
The maturity, product mix, complexity, and technological know-how of a food business will greatly impact where to start the Industry 4.0 food safety journey. Frontrunners might be faced with challenges related to technology and data, outdated systems, fragmentation, or data integrity and quality. Less mature food businesses will likely first need to deal with the lack of a digital strategy, quality and safety culture, and outdated systems.
What we have also noticed during our research is that smaller businesses, particularly new entrepreneurial startups, tend to be more flexible, open to change, and responsive to implementation of Industry 4.0 food safety technologies and systems, in part because the necessary investments are smaller (even though the overall cost barrier remains high). Larger food businesses might have more financial resources and technical know-how, but the required investment tends to be much larger due to the scale of the business operation and can be slowed down by internal bureaucracy.
There is no unique business profile to successfully implement Industry 4.0, and there are several good practices to make sure food businesses' investments are optimized regardless of the size or maturity level of the business.
We recommend that companies consider several steps when looking to effectively implement Industry 4.0 Food Safety technologies, as shown in Figure 3.

Potential Benefits of Industry 4.0
Although the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies for food safety is still in its infancy, we are already starting to see companies realize significant benefits from the adoption of a strong strategy. These include some of the following:
- Strengthening traceability and transparency capabilities
- Providing process assurance through repeatable processes that deliver food products with consistent and predictable quality and safety
- Allowing parametric release of products
- Bolstering predictive capabilities to enhance the resiliency of products and processes
- Supporting the continuous improvement of food quality and safety.
These benefits are enabled by real-time monitoring of products and processes, connected data, risk-based modeling connected across the value chain, and automation, as well as the right mindset and right behavior.
Recommendations
The opportunities to advance food safety through the adoption and implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies is vast, so long as it is done correctly. The food industry lags behind other sectors, but it can catch up quickly—and in certain cases, already is catching up.
When undertaking the Industry 4.0 journey, it is important to consider your investment options. For example, should the food business invest in a single, faster production line or two slower lines of production? The first option might be less costly upfront, in terms of capital expenditure, but in the long run food safety incidents (operational expenditure) could make it more expensive than the second option. Furthermore, it is easier to start with new production lines rather than retrofitting existing ones, but this is not necessarily more cost-effective. Hence, designing for the future, taking into account the long-term use of a new production line, and aligning this to the long-term financial and operational objectives of the business are fundamental.
People also play a key role in an organization's transition to an effective Industry 4.0 strategy. In the food industry, food safety often continues to be seen as a cost rather than an opportunity. This is simply not true, as we have seen with companies that have effectively implemented a strong Industry 4.0 strategy for food safety.
Shortage of digital skills and talent is one of the greatest challenges for companies trying to implement Industry 4.0 across all sectors. It is important for food companies to define the required skills and assess their skills gap. For Industry 4.0, skills in data analytics and statistics are fundamental to enabling the correct interpretation of generated data. This is in addition to strong food sector knowledge, which is why upskilling and training the current workforce and shifting to a digital mindset is fundamental.
Digitalization does not mean headcount reduction. Having the right technology with the right controls is not enough. Training must ensure that operators and food safety professionals are able to properly read data provided by the equipment and take corrective actions accordingly. Industry 4.0 technology should be seen as a solution that helps food safety professionals and operators do their jobs better, rather than replace them. It is an opportunity to demonstrate how attractive the food industry can be to work in and drive talent retention, especially in the current context of labor shortages in North America and Europe.
For further information, please refer to SSAFE's Industry 4.0 and Food Safety Guide,2 which is free to download.
References
- Schwab, Klaus. "The Fourth Industrial Revolution: What it means, and how to respond." World Economic Forum. January 14, 2016. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/the-fourth-industrial-revolution-what-it-means-and-how-to-respond/.
- SSAFE. "Industry 4.0 and Food Safety Guide." September 2023. https://www.ssafe-food.org/standars/industry-4-0-and-food-safety-guide.
Quincy Lissaur is Executive Director of SSAFE, a global nonprofit membership organization with the purpose of strengthening the safe supply and trade of food around the world.








